DEPARTMENT OF FORENSIC MEDICINE AND MEDICAL LAW
SCIENTIFIC WORK
Responsible for the scientific work of the Department of Forensic Medicine – Professor Andriy Bilyakov
Main directions of work:
(2019-2021) “Impact of Socio-Stress Factors on the Suicide Rate in Ukraine”.
From the creation of the Department “state of medical servise” at Saint Vladimir University, which provided teaching of forensic science, research has always reflected the needs of the forensic medical practice and direction of scientific research is explained by scientific talent of the Head of the Department.
The first Head of the Department, Professor І.F.Leonov published 6 scientific works, which concerned forensic medicine and epidemiology.
A characteristic feature of scientific works of Professor F.F.Ergardt was the practical direction. In his 52 scientific works Professor F.F.Ergardt highlighted the important issues of forensic medical practice and analysis of forensic examinations.
Professor М.О.Obolonskyi was the author of 33 scientific works. His textbook “Manual for the forensic medical study of the corpse and the study of material evidence” have been used studied for many years.
О.S.Ignatovskyi, who worked acting prosector of the Department of Forensic Medicine, in 1892 he submitted his scientific work “To the question of fractures of the skull” to a defence, after which he received a Doctorate of Medicine and was appointed Professor of the Department of Forensic Medicine of the University of Kyiv.
In 1893 student of Professor М.О.Obolonskyi – M.F.Kolesnykov defended his thesis on “Deaf in forensic medical examination “.
Further fundamental scientific research of forensic medicine character rehabilitated with the arrival at the Department of Yu.S.Sapozhnykov.
Describing the scientific products of the Department staff, which were carried out over the period of leading of the Department by Professor Yu.S.Sapozhnykov, we should note that scientific research has been the most important chapters of the theory and practice of forensic medicine, thanks to the most studies there were introduced many new and valuable data that contributed to the development of forensic science, which were usefully implemented in practice expertise, increasing the quality and scientific validity of the conclusions of the examination. The studies of Yu.S.Sapozhnykov can be divided into 3 groups: special research relating to different sections of the theory and practice of forensic medicine; studies of criminalistic direction of forensic medicine and studies, which are devoted to the organizational and methodological issues.
The main scientific direction, which is worked out by the collective of the Department of Forensic Medicine nowadays is a forensic medical diagnosis on the vitality and prescription of injury, the foundations of which were laid by Professor Yu.S.Sapozhnykov. All the scientific achievements of the scientific developments in this direction are connected with the name of Professor І.О.Kontsevych, which headed it as the Head of the Department of Forensic Medicine since 1970, and as the supervisor.
Scientific direction of the Department is one of the most urgent and complex problems of forensic medicine. And there was not accidentally that at the I, II And III all-Union congresses of forensic physicians (Kyiv 1976, Minsk 1980, Odessa 1988), at the plenums of the All-Union scientific medical society there was highlighted the need for research to create the diagnostic criteria for vitality and limitation of the occurrence of mechanical injury and noted the considerable progress in the development of this direction the collective Department of Forensic Medicine of the Kyiv Medical Institute named after academician Bogomolets. The development of this topic has also been recognized for the necessary by the Scientific Council of Academy of Medical Sciences USSR of forensic medicine.
As employees and researchers of the Department carried out a number of candidate and doctoral dissertations concerning this problem
The main direction of scientific research of Professor І.О.Коntsevych were the research in the area of establishing intravital strangulated furrows, which gave valuable results for forensic medical practice. This research formed the basis of the doctoral thesis «The expertise of strangulations» , which was defended in 1964 І.О.Коntsevych for the first time to identify intravital strangulated furrow, used a microscopic examination of nerve fibers in the area of the furrow, and the trunks of the vagus nerves in the place of their strangulation of the loop. These studies gave positive results: in the nerve fibers of the skin and the trunks of the vagus nerves in the field of intravital strangulated furrows there have been found reactive changes in the form of various forms of irritation, degeneration, and destruction, and in the trunks of wandering nerve – strain and rupture of the axial cylinders with creation incrustationsof neuroplazma at their ends curls etc. These changes were not revealed in the case of research after the death strangulated furrow. This study together with other data, which are at the disposal of the judicial physicians, of course, led to more precise and correct determination of intravitality of strangulation.
PhD thesis of Т.Ya.Pazenko, S.S.Bondar and О.І.Маrchuk were devoted to the study of morphological changes in intravital and after death abrasions, bruises and stab wounds using histological and histochemical methods of research.
Post graduate student of the Department Т.Ya.Pazenko in the MD thesis of (1973-1975) „Forensic medical diagnosis intravital and prescription of the appearance of the abrasions” (1977) convincingly proved that such widely featured signs of intravital as capillary hemorrhage and hyperemia are observed not only in intravital, but in after death abrasions. These features should be considered together with other signs intravital reaction. Morphological features of the regional standing leukocytes in intravital scratches appear during 1 hour after injury, and leukocytic infiltration in 3 hours. According to T.Ya.Pazenko one of the earliest symptom of intravital tissue reaction to the mechanical trauma, unlike after death, is the presence of connective tissue cells with high activity of alkaline phosphatase, who appear in injured skin after 10 minutes after the abrasion, which is explained by the intensification of energy metabolism in the injured area. Ya.Pazenko published 19 scientific works, which are devoted to intravitality and limitation of the appearance of injuries of different types and other issues.
A post graduate student of the Department A.I.Marchuk (1976-1979) in his thesis «Histo-enzymology indicators in the diagnosis of intravitality and prescription of stab wounds» (1979) was the first, who investigated the morphological characteristics of intravital and after death stab wounds liver, lung, heart and skin at various terms of their infliction. He convincingly proved that in intravital wounds unlike after death was defined violations of indicators of redox processes of energy and carbon-phosphorus metabolism near the vascular and general tissue reactions histo- and enzyme histochemical. In the dynamics of histostructural changes there was clearly defined organ specificity of reactions, the severity of which depends on the prescription of causing wounds. During his work at the Department А.І.Marchyk published 32 scientific works, which concerned different issues of theory and practice of forensic medicine.
PhD thesis of postgraduate student of the Department (1978-1981) S.S.Bondar was dedicated to «Complex study of bruises to establish intravitality and prescription of their infliction» (1982). In this work for the first time using a macroscopic, histological, histochemical and enzymology methods of investigation there was established that in intravital bruises, unlike after death, consistently develops complex morpho-functional changes, which developed itself vascular, hematogenous-cellular reactions with the presence of early (10-60 minutes after injury) typical changes in the vessels of microcirculation, metabolism disturbance, that were expressed in qualitative changes and redistribution of protein-carbon compounds in the composition of the basic substance of the blood vessels and connective tissue of the dermis and hypodermis. Such changes cause increased vascular-tissue penetrability, dynamics of changes in the activity of non-specific phosphomonoesterase, dystrophic changes of fibrous structures with following development of reparative processes.
The study of the specified problem by Т.Ya.Pazenko, А.І.Маrchuk and С.С.Bondar demonstrated that skin injuries, inflicted in the nearest terms ante – and after death periods in their morphological and morphochemical characteristics are similar to each other and therefore their differentiation by histological and histochemical methods is not possible. In addition, the use of morphological methods of research in expert practice, according to the results of their finished work, limited by the fact that such research can be used during studying only fresh forensic material in which there are not effects after death autoliza.
That’s why there was arised the question about application of a different approach to diagnosis intravitality and prescription of the appearance of injuries. In search of ways to solve this problem assistants B.V.Mykhailychenko and V.A.Sushko have used biochemical methods of research of mediators of inflammation, which is the basis of forensic medical diagnosis intravitality and prescription of local injury.
In particular, B.V.Mykhailychenko for first time in his thesis “Determination of intravitality of mechanical injuries to the quantitative content of free histamine of injured skin” (1987) developed a “Way to obtain free histamine from the injured and uninjured skin” (A.S. No 1174856), he also studied the quantitative content of free histamine in intravitality and after death mechanical injuries, which were inflicted in the early stages of ante – and after death period. He established that the content of free histamine has significant regional and individual fluctuations, at the same time as the symmetric and adjacent to the injured parts its level is equal. He has proved that the level of free histamine in intravital injuries of more than 1.2 times higher compared with intact skin, which should always be explored as a control. Moreover, the level of increase of free histamine depends on the type of the injury and its prescription that allows us to specify the terms of its appearance. From a practical point of view, it is very important the fact that free histamine in injured and intact skin can be detected not only in fresh tissues, but in the tissues with significant putrid changes.

Assistant B.V.Mykhailychenko demonstrates methods of identification of histamine to Professor I.O.Kontsevych
and Associate Professor V.A.Shevchuk, 1985
During research on the topic of PhD thesis B.V.Mykhailychenko published more than 20 scientific works, including abroad, has developed 2 inventions, 2 information letters, much of innovations. In 1988 B.V.Mykhailychenko approved a topic of his doctoral dissertation, the scientific adviser was appointed Professor I.A.Kontsevych.
V.O.Suchko in the thesis on the topic: «The forensic medical value of determination of free serotonin in injured skin for diagnose of intravitality and prescription of mechanical injuries» (1987) developed a method of determining the free serotonin in injured and non-injured skin. He proved that free of serotonin has significant individual and regional fluctuations in non-injured human skin, and its level is the same on symmetric parts, which allows there to use as a control. Content of free serotonin in areas of skin with intravital mechanical injures, is not less than 1.5 times higher comparing with non-injured skin. Moreover, free serotonin can be detected not only in fresh tissues, but in the tissues exposed to putrefactive changes that are extremely important for forensic medical practice.
In 1994 Assistant І.А.Fedotova defended her thesis on the topic: «Morphological criteria of forensic medical diagnostics of main etiological options of shock» in which for the first time there were studied the structural changes in the organs and tissues of the corpses of persons who have died from clinically diagnosed cardiogenic shock and allergic shock and there were received morphological criteria for differential diagnosis of hemorrhagic and traumatic shock. He published 6 scientific works on the theme of dissertation.
Summarizing the numeral domestic and foreign scientific literature on the problem of diagnostics intravitality of local injury, Professor I.O.Kontsevych and her student MD B.V.Mykhailychenko noted that despite the variety of aspects of diagnostics, which are based on the tissue, cellular, enzyme, molecular and many metabolic symptoms of local inflammation as a universal answer to the impact of external factors, all of them depend on effects of physiologically active substances, which locally produced. Exactly in this area of scientific research there was decided to develop further diagnostics intravitality of injury. In 1992 B.V.Mykhailychenko defended his dissertation work on the subject: «Complex biochemical diagnostics of indicators of reactive changes of the injured skin for diagnostics of intravitality and prescription of injuries» at the Institute of Forensic Medicine ( Moscow). In this scientific study for the first time there was carried our research of the content of such physiologically active substances, as free and acid-extracted fractions of histamine and serotonin, free fractions of heparin, amino acids, prostaglandins F2 and E2 and also chemical elements zinc, magnesium, calcium, lithium. B.V.Mykhailychenko has proved natural and consistent changes in their quantitative content due to intravital injury that allowed to develop new diagnostic criteria of intravitality and prescription of injury – schedule biological change in the contents of physiologically active substances in mechanical injuries of the skin.
In addition, for the first time there were developed a way of parallel determination of biogenic amines in assay, ways to analyze the content of free heparin and free amino acids in the tissues, detection of prostaglandins during their thin-layer definition.
For the first time, there was conducted research of mummified tissues from the centuries-old corpses, it allowed to find out a question about presence in them of physiologically active substances. The results of this scientific work were quite actively tested not only at national conferences, and during forensic medical forums abroad (Dresden, 1989; Tokyo, 1989; Bogota, 1990; Adelaide, 1990; Florence, 1990; Berlin, 1991). There were received 2 Certificates of the USSR for inventions on the materials of thesis: «Method of determination of intravital tissue injuries in a corpse» (A.C. No 1405810) and «The method of secretion of free amino acids in tissues» (Patent of Russian Federation No 2063759) and 4 certificates on rationalization proposals.
Direction of scientific research, which was started by Professor I.O.Kontsevych, since 1991 was continued by the Head of the Department, MD B.V.Mykhailychenko: developing signs of intravitality of injury and clarifying the diagnostic indicators of general reaction of the human organism to external effects through the application of biochemical researches.
In 1996 a postgraduate student of the Department Asaad Таhera (Kuwait) defended his thesis «Forensic medical diagnosis of intravitality of hanging for the crystallographic structure of biological fluids» (Associate Professor B.V. Mykhailychenko was his scientific supervision); in the dissertation Asaad Таhera continued to study a question of determination of intravital mechanical asphyxia by crystallographic studies of body fluid – spinal fluid, pericardial fluid, blood and tissue extracts strangulary furrow during hanging.
Taking into account the fact that during the asphyxia there were appeared considerable and important metabolic disorders in a body, especially, in body fluids, crystalogram (tezigram) is the integrated visual indicator of these metabolic disorders. For the first time author determined the natural character of crystalograms’ creation of biological substrates during hanging, and he proved that at the same macromorphological signs of a fast death, which is considered as general asphyxial signs, in the case of mechanical asphyxia and sudden death from cardiovascular disease, metabolic changes in the body differ on a crystallographic picture during these two types of death. The results of the thesis are presented in 3 scientific papers, the invention «Method of diagnostics of the intravitality of mechanical asphyxia by hanging» (Declaration patent of Ukraine for invention № 24434) and 2 rationalization proposals.
Assistant A.M.Biliakov in his MD thesis on the subject: «The forensic medical value of catecholamines for diagnostics hanging», which he defended in 2002, for the first time taking into account the role of catecholamines as biologically-active substances, that taking part in the pathophysiological mechanisms of development of asphyxia and influence on the cardiovascular system, brain and involved in a traumatic process in injured skin by loop, proved their diagnostic value for complex forensic medical diagnosis of intravitality of hanging as for the content of catecholamines in liquor and pericardial liquid and in strangulated furrow.
An important aspect of the study was revealing the prevalence of coming catecholamines lesions infarction at the moment of hanging, which is important in the cases of resuscitation and provide medical care to victims, which was taken out of the loop in time.
As a result of the conducted research there was proved that in the case of sudden death from acute form of coronary heart disease there was significantly increases the area of catecholamines myocardial injury in the right atrium, right ventricle, interventricular septum, left ventricle, then in patients with chronic coronary heart disease.
According to the results of dissertation researches he has published 4 scientific works, received 2 patents on the invention «The method of getting fractions of catecholamines from biological tissues» (Declaration patent of Ukraine for invention № 41214) and «Method of diagnostics intravital hanging» (Declaration patent of Ukraine for invention № 50491).
An assistant of the Department I.O.Artemenko in his MD dissertation «Biogenic amines as the criterion for defining asphyxiant state at the various types of mechanical asphyxia» for the first time proved the possibility of diagnosing of asphyxiant state at the various types of mechanical asphyxia on the basis of quantification of biologically active substances histamine and serotonin in the cerebrospinal fluid in the cervical cord, lateral and terminal ventricles, pericardial fluid and tissue of the lungs.
On the topic of dissertation research O.I.Artemenko received 2 patents of Ukraine for useful model Patent №25877 “Way of getting cerebrospinal fluid” and Patent № 27733 «Device for getting of cerebrospinal fluid».
Professor B.V.Mykhailychenko considerable provided with scientific support the departments and faculties (courses) of forensic medicine of the higher medical schools of Ukraine by scientific supervision of the dissertations. So, under his scientific supervision S.M.Fedorchuk defended his Ph.D. theses on the topic: «Value of somatotypes in forensic medical diagnosis of the common features of the man» (defended in 2004, Ivano-Frankivsk State Medical Academy), I.G.Savka on the topic: «The define of a forensic medical criteria fractures short tubular bones brush during injuries caused by blunt objects according to the data of clinical, morphological, experimental and expert studies» (defended in 2004, Bukovyna State Medical Academy), L.O.Yalanska on a topic: «Forensic medical evaluation of acute blood loss taking into account features of the blood supply of the internal organs» (defended in 2002, Ukrainian medical stomatological Academy), D.V.Kostyleva on the topic: «The forensic medical role of immunoglobulins in serum of cadaveric blood in the differential diagnosis of causes of death» (defended in 2003, Lugansk State Medical University), R.G.Kryvda on the topic: «Identification of the person in forensic medicine based on PCR analysis of genomic DNA bone» (was approved to execution in 2005-2008 by Odessa State Medical University).
Now Assistant Professor of the Department of Pathology and Forensic Medicine I.G.Savka under the scientific supervision of Professor B.V.Mykhailychenko is working on his MD dissertation “Forensic medical justification mehanogenez and morphological characteristics of fractures of the long bones of the lower extremity, taking into account their structural-functional characteristics”.
After the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, the Department of Forensic Medicine of KMI took part in determining the question about the presence of radionuclides in the human body and the influence of small doses of radiation exposure on sudden death inhabitants, Kyiv.
At the same time N.M.Portianko studied in clinical residency of the Department, which studied (on equipment of the Academy of Sciences of Ukraine) the presence of radionuclides in the body of the deceased, who lived in the 30 km zone. In the collected by her forensic material – the internal organs of the deceased persons with the help of two independent research methods – histoautoradiography and raster electronic microscopy there were detected radionuclides, and by x-ray microanalysis of hot particles there was explained their range. Comparing their range of literary data, there was found out that the elemental composition of the hot particles, which were located in the lung tissue of deceased, coincides with the composition of the particles, which were found in the environment after the accident at ChNPP and also with the isotopic composition of the blood of the patients who worked at the plant during liquidation of the accident consequences. The activity of these hot particles on alpha-, beta – and gamma-rays could exceed 1х100000 Bq. Hot particles were in the lung tissue, even after 2 years after the accident.

Radioactive particles („hot particles”) in the lung tissue
Associate Professor of the Department B.V.Mykhailychenko in collaboration with the Institute of Environmental Pathology carried out a statistical analysis of sudden deaths of residents of Kyiv in the period of 1981- 1991 in order to find out the influence of the “ Chernobyl factor” on mortality from certain diseases.
Associate Professor V.A.Shevchuk and senior lecturer А.S.Lisovyi are authors of many scientific works, including inventions, which are devoted to the mechanism of formation of craniocerebral trauma and prescription of its injuring. This direction they developed in cooperation with the Institute of neurosurgery of AMS of Ukraine.
Working on the problem of prescription of occurrence of traumatic brain injury in forensic respect, along with the study of cardiovascular and destructive changes in the area of brain contusion there were investigated infringement of metabolic processes in the tissue.
So, in the next few hours after craniocerebral trauma in the brain injury happens minor reduction of the activity of SDG, MDY, LDH, and OVER- diaphorase in nerve cells and astrocytes, and in the endothelium of the capillaries and precapillaries – a slight decrease in the activity of alkaline phosphatase.
The activity of these ferments decreased on the second or the third day after the injury, what is result of the next destruction of brain tissue and the formation of the zone of necrosis with unbalance of glycolic cycle.
Traumatic brain injury may be accompanied by the formation of the upper subendocardialnah hemorrhages, whose origin can be explained by the rapid fall in blood pressure at the time of the secondary stem bleeding.
The presence of the upper subendocardialnah hemorrhage during identification of secondary hemorrhage in the brain stem in cases of traumatic brain injury, gives the possibility of accurate differential diagnosis of the sequence and prescription of bleeding in the parts of the brain stem (inventor’s certificate of the USSR № 1683689 for the invention «Method for the diagnosis of secondary hemorrhage in a brain-stem death from craniocerebral trauma.
These and other statements are exposed in the monograph «Clinical and forensic medical examination of traumatic brain injury» (1996) and the manual «The forensic medical neurotraumatology» (2003).
From April 1988 staff of the Department of Forensic Medicine was involved in research work on a topic «Complex research of mummified remains, their conditions of storage and exhibiting of the Kyiv-Pechersk Historic-Cultural Preserve ». This work was carried out in accordance with the decision of the Presidium of the Council of Ministers of the USSR (February 28,1985), the Kyiv City Council (June 17,1985), and the Bureau of the Presidium of the scientific Council of Ministry of Health of the USSR (January 29, 1988), which expected the necessity to examine the question about the methods of preserving the mummified remains, which are unique exhibits of the interior of the cave of the Kyiv-Pechersk Preserve of world importance. Professor І.О.Коntsevych was approved the scientific leader of this work by the Presidium of the Academic Council of the Ministry of Health of the USSR (January 28, 1988).
Researchers had had the following tasks face during investigation:
- To examine the causes of the different states of mummies.
- To develop optimal saving conditions and exhibiting them in the cave labyrinths.
- To find out the nature of the origin of mummies.
- To determine prescription burial of mummies.
- To carry out personal identification of the most famous historical figures, such as Ilia Muromets, Nikon Sukhyi, Alipii-iconographer, Agapit-doctor, Nikon-hegumen and others, comparing of received scientific medical data with the famous historical data, which contained in the Kyiv-Pechersk Paterikon.
- To make a singular „medical certificate” for every mummy.
Diversity of the issues, that need solutions, has caused the need to engage to the scientific development of different specialists. In connection with it there were involved 25 experts to research work including employees of the Department of Forensic Medicine, anatomy, radiology, biochemistry, General hygiene KMI and also scientific employees of research institutes of NAS of Ukraine – Department of Zoology, Geology, Microbiology and Virology of MOH of USSR.
To develop optimal saving conditions and investigate the reasons of different conservation mummified corpses there was conducted hygienic study of conditions of a microclimate and air environment of the near caves, the study of fungal and bacterial flora, entomofauna of mummified remains, sarcophagi and labyrinths of caves in different times of the year taking into account of different tour load.
Hygienic study of microclimate and air environment, that was held by Associate Professor of the Department of General hygiene KMI I.I.Nikberg, consisted of the definition of air temperature, relative and absolute humidity, air velocity, carbon dioxide and total content of non-completely oxidized substances in the air of caves. As objects of research were selected four rooms, placed in different operating conditions areas of the caves, the church “Vvedenia”, Trapezna Church Varlaam’s church, Anthony Church, where there was conducted three times a day measurement of indicators microclimate in the days of research (9:30, 14:00, 17:00).
For a retrospective analysis of the peculiarities of the dynamics of indicators of temperature-humidity regime there was carried out a statistical analysis of about 10000 primary registration data of temperature and humidity in the premises of the nearer caves during the period from 1981 to 1987. During it there were calculated the absolute average daily, ten-day, month, seasonal and annual temperature and humidity changes in the values of these indicators over the same time period.
There was revealed (by analysis) that the average daily temperature values are between +7 0 C to +19 0 C, relative humidity of 75 to 99%. The lowest temperature is observed in winter and spring. The coldest is Trapezna Church, the warmest – church of Varlaam”. The highest average humidity was in Trapezna Church. The most significant changes in humidity were in it and also in the Anthony Church
Studies have shown that the main factors that create negative conditions for the preservation of exhibits and temporary stay of the visitors are:
– high humidity of air up to 97,2-100%;
– instability and considerable daily and seasonal fluctuations in air temperature;
– high content of carbon dioxide in the air (0.1 to 2% at the rate of 0.04%).
For optimal temperature and humidity was proposed:
– to make set geohydrology actions that would completely exclude or minimize soil moisture secretion;
– to limit the number of visitors (no more than 2000-2500 per day, 30-minute excursions and cross-sectional stay in the caves of not more than 150 persons);
– to ensure effective artificial air exchange.
The best and possibly the only way of providing the optimal parameters of the air environment that is required (in conditions of a real tour load caves), except hydrotechnical actions, is using of the delivery system and automatically adjustable output parameters, conditioned air.
According to performed calculations, mechanical ventilation system should provide (with the number of visitors is not more than 2500 people per day and 8 hours of work) getting into the cave is not less than 7100 m3/day of fresh air.
The study of fungal flora mummified remains and labyrinths of the nearer caves was conducted by the Institute of Microbiology of the MOH of USSR by senior scientific employee T.I.Redchyts and a senior engineer R.Yu.Pashkevych. For mycological analysis were selected the samples from the labyrinths (ground, walls, floor, indoor air) and exhibits (air of sarcophagi, wood, fabric and also samples from the skin, the naked bones and tissues of a mummy). Samples of air labyrinths received after the maximum tour load and without it in the spring, summer and autumn periods of the year.
Among the samples from the walls of the labyrinths there were prevailed isolates of type penicil and aspergil. There were met samples, which had only penicils or only penicils and aspergils. The frequency of some of them is amounted 73.3%.
From the samples of soil were secreted the ordinary representatives of micromycetes, which are typical to this ecological niche: penicils, aspergils, trichoderma and isolates other types, except fusariums.
Among the samples from the floor, compared with other ecological niches considerable increased the specific gravity of mucolar fungi, although penicils remained dominant.
Air labyrinths of caves concerning the composition of micromycetes in the spring-summer period was slightly differed as by quantitative and qualitative composition. Penicils, aspergils and dark colored fungi were dominant. Depending on the area of labyrinths were revealed some differences in quantitative and qualitative composition of micromycetes. So, in some areas (Trapezna Church, cell demoniacs, in cell with skulls and in the cell with slide) there were prevailed isolates of mycelia sterilii, sometimes there were met isolates other genus – aspergils and alternarias. In areas of caves that have operational load, there were identified isolates of many types, but penicils and aspergils were prevailed. Moreover, their number in the period of maximum operational load was increased almost in 2 times. In autumn these differences somewhat were smoothed out, but the qualitative composition was more diversified than in the spring and summer. More frequent there were met representatives of different genus of the family of demacia genus aspergillus, including group aspergilius femigatus and aspergillus flavus, among which, according to the literature, there were often met pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic and toksykology representatives.
The results of mycological research of mummified remains showed that myxomycetes, which were revealed on the mummies, were representatives of the genus rhizopus, penicillium, aspergils, trichoderma and others, which grow, develop and spore carry using the substrate, destroying it. We should note that comparing with other ecological niches, there were dedicated an increase specific weight of fungi order micoralie on the mummified remains and also in the samples of the floor. According to the literature separate genus, which were dedicated on the mummies are toxigenic, conditionally pathogenic and pathogenic.
Study of bacterial microflora of mummified remains, fabrics, sarcophagi and also air, floor, walls and soil labyrinths of the nearer caves was conducted by employees of the Institute of Microbiology and Virology of the AS of USSR senior engineers K.V.Таntsiurenko and A.V.Sheremet.
Study of bacterial contamination of air of near caves was conducted in 8 places of labyrinths during the movement of the tourist’s hall at the entrance, descending the stairs, Anthony Church, Church of Varlaam, Trapezna Church and a passage near the tomb Аlezia, staircase to the exit, Khrestovozdvizhenska Church.
Research were conducted in the days of the tour with a maximum load and without it.
The results of a study of air micro flora has demonstrated that in spring, summer and autumn of 1988 microbial numbers in different places labyrinths of caves were in the range from 1000 cells/m3 to 7000 cells/m3.
The results of the study demonstrate a clear correlation of microbial number of air with the number of visitors of the nearer caves. With the increase of the tour load is increased bacterial number in 2-3 times compared to the weekend of the Museum.
Also, there was observed the relative stability of bacterial number of air in such places of labyrinths as Anthony Church and Trapezna Church. Maybe because of tourists did not visit them so often, this relative stability is up to 2000 cells/m 3. In addition, it can point out to a weak currency air in these «dead-end» places labyrinths, which helps to increase humidity in these places.
In process of visual and microscopic entomological research of skin mummies and destroyed tissue into powder mass, which was carried out by senior researcher of the Institute of Zoology of the Academy of Sciences of the AS USSR A.A.Petrenko, there were identified small remains pupae flies and sometimes entire instances, fragments of the beetles of the gravediggers, pupae of flesh-eating beetles, body beetle- staphylinidae, fragments of bodies of acaroid mites and large insects in different proportions and amount. Among the destroyed tissues of Ilia Muromets was even found mummified corpse of a bat.
Puparia of flies and their fragments, the remains of larvae and adult flies belong to necrophile flies, larvae of which develop in the first stages of decomposition of a corpse.
Among the discovered fragments of the bodies of insects and mites, the larvae of flesh-eating beetles and adult beetles, which eat dry and getting dry substrates of animal origin, can cause the most destructive affect to mummified tissues as. Predatory staphilinid beetles (the remains of their bodies were on many mummies) can eat due to other living insects here, especially, larvae and pupae flies, mites and other invertebrates, so their activities is directed at regulation of the number of insect destroyers of mummy tissues.
Identifying the mummified corpse of a bat among destroyed tissues mummy of Ilia Muromets is connected with its inhabitation in the environment and accidental hit to mummies.
We should note that any living stage of development of the insects and mites on the mummies were not found.
There was conducted a complex research of 20 mummies to study the state of saving of the mummies and their «certification» of funeral terms.
During research of each mummy there were used morphological (macro – and microscopic), anthropometric, x-ray, biochemical, in particular – fluorometric, x-ray fluorescence, atomic absorption spectrophotometric method «protein hours, and previously specified mycological, bacteriological and entomological research methods.
Morphological studies, which were performed by Professor І.О.Коntsevych, Associate Professor S.S.Bondar, assistant I.A.Fedotova (the Department of Forensic Medicine), Associate Professors О.Z.Lopushenko and L.I.Ostapiuk (Department of Normal Anatomy) revealed that the mummies are the corpses of men in the form skeletons, which covered with dense dry skin of amber color. Degree of saving of the mummies is different: some of them – Ilia Muromets, Agapit, Nikon Suhyi, Nikon, Hegumen of Pechersk, Nicodym, Isaakii were saved better , others – Kuksha, Slipii, Nyphon – worse, and some Sylvestr, Yefrem, Isaia, Аvramii are heavy destroyed and presented in the form of separate bones, interconnected by wisps of mummified tissues. In most tissues, even during good saving, skin-muscle coverings and tissues in the lumbar region had been destroyed. In some mummies of the torso and limbs were skeletal. Internal organs have not survived in any mummies, which were investigated. It should be noted that on the surface of the mummies, especially in the posterior-lateral surfaces of the body and extremities, some parts of the skin were damaged by fungi, and also insects, in particular, flesh-eating beetles, as a result, skin covers had a network structure. The hair on the head, face (moustache, beard) and pubic was well saving only in a few cases. Hair was of different length, yellow, brittle and during microscopic examination were alien layers on its surface, but the hair structure was clearly differed.
It should be noted that there was found penetrating longitudinal form wounds with smooth edges during study of mummies Ilya Muromets in the left part of the chest and on the back surface of the left hand.
In some mummies there were found traces of the old intravital injuries of the bones of the cranial vault (Nykon Suhyi, Kuksha), and also traces of accrete rib fractures in Ilya Muromets in the form of bone corns.
Using anthropometric studies there was investigated the type skull, race, age, length of the body. Calculation of height was carried out according to the long tubular bones according to the calculation formulas Troter and Glezer (1958) for men-caucasoids during study of partially skeletal corpses. Studies have revealed that mummies were average or above-average height, age of persons before the death fluctuated within 45 – 60 years, and in separate cases – up to 30 years, they all belonged to the caucasian race.
In some mummies during radiological research, which was carried out by Professor Т.V.Topchii was found atrophy of the alveolar process, periodontitis injures and it explains intravital loss of many teeth; some of them discovered signs of deforming spondylarthrosis, mainly in the lumbar and sacral parts (Ilya Muromets, Agapit, Sylvestr); ankylosis after suffering a knee arthritis (Nikon Suhyi).
Professor I.O.Kontsevych made histological examination of skin-muscular covers and it revealed that the layers of the dermis and underlying tissue were not differ, preparations were presented by fibrous structures with a large number of homogenized fibers, which were pressed in the form of layers and were hyperchrome coloured on different colours.
There was revealed a great number of different forms, often rounded, alien particles of dark amber or black on the surface of slices and between the muscle fibers of all investigated mummies. Their presence was possibly caused by leakage of tissues of any substances that could be used with the purpose of saving of dead bodies. Interesting is the fact of detection in some cases, despite centuries-old, blood vessels and their injury of the atherosclerotic process (Simon Suzdal). In preparations of many mummies (Ilya Muromets, Nykon Pecherskii, Sumon Suzdalskyi, Nykon Suhyi, Agapit) on the surface of slices and intermuscular fibers were found chlamydospores and mycelium threads of fungi, whose identification was carried out by mycologist of Research Institute of Microbiology and Virology, Ministry of Health of Ukraine.
It was very interesting to investigate the possibility of saving such biologically active substances such as histamine and serotonin in mummified centuries ago tissues, which are reliable markers in deciding concerning chronobiology of injuries. Assistant B.V.Mykhailychenko determined their availability and quantitative content by the fluorometric method in exalbuminous extracts of mummified tissues of different regional areas of mummies in accordance with developed at the Department of Forensic Medicine techniques that have been protected by the copyright certificate on the invention and the evidence on industry innovation proposal. Studies have demonstrated that histamine and serotonin, quantitative content of which, in some cases, had regional features, revealed in mummified tissues. It should be noted that the level of histamine and serotonin in the wounds in the chest and left hand in the mummy of Ilya Muromets was considerable above the control that allowed to consider these injuries intravital.
There was carried out roentgen-fluorescentic detection of chemical elements with further confirmation of their quantitative composition by atomic absorption spectrophotometric method for studying the inorganic compound mummified tissues. These studies were performed by the assistant of Department B.V.Mykhailychenko and scientific employees of the Institute of Geology of Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR O.B. Lysenko and B.P.Melnychenko. In the result of the research they found out that there are chemicals such as zinc, rubidium, iron, copper, lead, mercury, bromine, manganese, calcium, and tungsten in mummified tissues. Moreover, the content of these chemical elements in mummified tissue of Alypii-icon-painter was so high that they were out of the of measuring range roentgen-fluorescentic analyzer. It is quite possible that the accumulation of these elements in the tissues of the deceased was the result of prolonged contact with the substances, maybe with paints, which were included in them.
There were found considerable concentrations of manganese, bromine, zinc and lead, unlike other chemical elements (which were in trace quantities) in mummified tissue Agapit-doctor. We can assume that the accumulation of these chemicals in the tissues of the deceased could be associated with the occupation – medicine care, because they can be active substances of medicines.
These data allow us to confirm the affiliation studied mummies Alipii-icon-painter and Agapit-doctor, information about which is stored in the Kyiv-Pechersk Paterikon.
One of the difficult tasks, that study group needed decide, was to determine the possible prescription of burying of each mummy. There is no information about the methods of determining the prescription of burying mummified corpses in the literature, although this problem is widely developed by domestic and foreign researchers as well. Despite receiving valuable results of the laws of development after death processes, they could not use research methods during studying the mummified corpses. In search of ways to solve this problem there has been studied many necessary materials of such sciences as archaeology and geology, which is developing the dating of fossil material.
These methods had a special interest because there are objects of biological origin in the fossil material, their dating terms of burying are carried out due to a number of biochemical parameters. Taking into account that the mummified tissue saves some of its biochemical characteristics for a long time, and their processes of disintegration of protein are slow, there was decided to investigate the dynamics of changes of amino acid composition in the temporal aspect method protein hours and determine the ability to solve the problem.
Biochemical studies of amino acid composition of mummified tissues were performed by using the analyzer «Biotronyk» (Germany), integrator CF – 3A company «Shymadzu» (Japan) of employees of the Institute of Geology of Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR O.B.Lysenko and V.P. Melnychenko. After decryption of chromatogram were calculated qualitative and quantitative characteristics of amino acid spectrum of mummified skin and also a number of amino acid parameters, which reflected the speed and extent of the processes of change with time of the organic matter.
In the course of the research there was established that the level of the amino acid composition of mummified tissues had regionary and individual characteristics. There was proved that the characteristics of their amino acid spectrum are being changed and correlate with the antiquity of a burial place. Terms burial of mummies were defined and corresponded to XI, XII, XIII century and were correlated with the data of the Kyiv-Pechersk Paterikon.
A complex research of 20 mummified remains allowed to investigate their height, age, race and presence or absence of pathological processes and injuries of the locomotor apparatus, set a possible prescription burial, and also find a number of other characteristics and perform their personal identification with the historical materials that have been saved.
There was made «passport or each investigated mummy which together with historical information contained results of all completed studies and also macro and microphotography, x-rays, hromatograms and other illustrative material.
So, in the process of the research there were received interesting scientific the results, which did not have analogues in domestic and in foreign scientific literature as well.
The importance and necessity of the research is that the unique exhibits – the mummy of centuries ago – were studied integrated and in details for the first time, that has a valuable cultural, historical and educational value.
In 1995 Professor I.A.Kontsevych, MD Mykhailychenko, Associate Professor of the Department of Anatomy of our University L.I.Оstapiuk and Head of the medical-criminalistic Department of the Kyiv city bureau of forensic medical examination Ju.M.Kovalenko carried out somatoscopy study of the skulls of a thousand years ago, which were found during excavations on the territory of Ukraine and now they are in the collection of the Institute of anthropology of the Academy of Sciences of Ukraine. The purpose of this study was to define the morphological features of the skull, injuries, their origin, signs of healing of injuries and possible human life after injury.
The study revealed that in giving skulls there were injuries of traumatic nature in the form of a perforated defects caused by a blunt object and injuries caused by a scrape object with a sharp edge, which were reminded trephining holes.
Any signs of bone reparation for injuries caused by a blunt object was not found. At the same time, injuries of the bones of the skull, which were caused by the subject of sharp-edged and sharp scrape edge had signs of reparations of the bone. This gave the opportunity for making a conclusion (taking into account the degree of reparations) about the duration of human life after the injury, which could last as two months and more than 1 year. There were given 3 silicon knives for carrying out the research, which were found during excavation and by which could be caused trephining holes in the skulls. These knives were made experimental holes-injuries on a skull for 15-20 minutes.
So, the ancient people of the past thousand years made trephining holes in skulls by a blunt object with a sharp or sharp scrape edge, which would be a simple silicon knife.
In 1999-2000 – the Department carried out scientific-research work on a topic: «to conduct a study of the efficiency of alcohol analyzers „LION ALCOMETER SD – 400” and „ALCOBLOW” to determine the content of steams of alcohol in exhaled air». According to the research it was found out that the devices „LION ALCOMETER SD – 400” and „ALCOBLOW” by their functional possibilities correspond to the medical recommendation for the analysis of alcohol in the exhaled air and give the possibility to determine the existence and amount of alcohol in the blood and, therefore, determine the level of alcohol intoxication. Analysis, which is conducted by these appliances is specific for the detection of alcohol vapors. Devices determine not only such alcohol as ethanol but also methanol and technical alcohol-containing liquids.
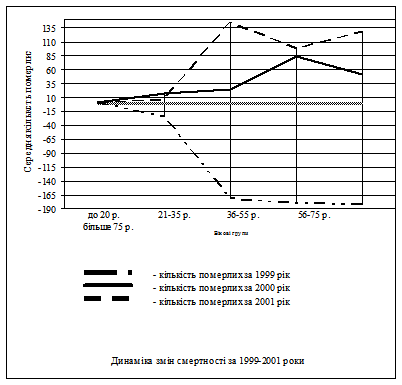
During 2001-2003, the Department of Forensic Medicine studied the possibility of sudden death among residents of Kyiv.
There was found out that there is an increase of mortality of inhabitants of Kyiv from cardiovascular disease with the deterioration of weather factors – increase of air humidity, wind speed, fluctuations of atmospheric pressure, especially in January, may and December, when additionally influenced by factors such as holidays, alcohol, overeating.
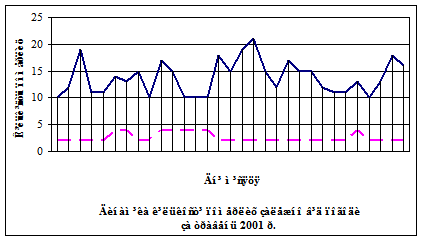
In 2001, the number of deaths from cardiovascular diseases is conciderable exceeded the same indicator of previous years.
Since 2003 the Department of Forensic Medicine is carrying out scheduled scientific thematics of pedagogical directions. In 2003-2006 there was performed a research work on the topic «The using of test control for optimization of educational process and objectivity of assess students’ knowledge during studying the basics of forensic medicine.
There were conducted research of progress of 994 students of the 5th year of medical faculties during studying the basics of forensic medicine, and research have revealed different levels of knowledge of current topics of practical training. The best of all students learned educational material concerning the forensic medical trauma: injuries caused by a blunt and sharp object, mechanical asphyxia, gunshot wounds and such topics such as the expertise of biological material evidence, expertise in cases of pharmaceutical cases. The topic “medical and forensic research methods” had a little lower index; it is explained by the fact that this topic has forensic direction and is differs from the topics of medical profile. This topic demands from the students not only knowledge of the issues of forensic medicine, but also to remember the laws of physics, chemistry etc.
Poor level of knowledge of the material, which is related to the out-of-school study (barotrauma, injuries caused by electric shock, injuries caused by acts of extreme temperatures, injuries from the effects of ionizing radiation) requires from the lectures to pay more attention to this issue, provide students with consultations and etc.
From our point of view a little lower level before the test control – 3.5 points is a stimulating factor for the preparation to the differential exam, point of which was above the 3.9. Therefore, introduction of the test control in the educational process at the Department of Forensic Medicine of NMU improves the quality of knowledge of the basics of forensic medicine and increases objectivity assessing students’ knowledge.
From 2007 to 2009 the Department carried out the planned research work on a topic: «Methodological substantiation of the effectiveness of individual students’ work during studying the fundamentals of forensic medicine in accordance with the requirements of the Bologna system of education».
This research topic has allowed to the Department and all the lectures to prepare for the teaching of forensic medicine in the conditions of the credit-modular system of training, which is actively implemented at the Bogomolets National Medical University.
Since 2010 the collective of the Department of Forensic Medicine have been performing the planned research work on a topic: “Study of the components of the final module control as assessing the level of knowledge of forensic medicine and medical law by the students of the 4th year of medical faculties of NMU”.
In September 2009, the Sofia Kyiivska National Reserve began the scientific study of remains from the sarcophagus of Yaroslav Mudryi in St. Sophia Cathedral. Professor B.V.Mykhailychenko and Doctors of Sciences S.P.Segeda, who developed the scientific research program and created the scientific team of experts for their conduct, were invited for scientific leading of these research.
The research group included, in particular, MD, assistant of the Department of Forensic Medicine A.M.Beliakov (the Department of Forensic Medicine of the Bogomolets National Medical University), Professor V.G.Cherkasov, Associate Professors I.V.Dzevulska, O.I.Kovalchuk (Department of Human Anatomy of the Bogomolets National Medical University), Professor T.V.Topchii (Department of Radiology and Radiation Medicine of the Bogomolets National Medical University), MD, assistant D.V.Topchii (Department of Surgical Stomatology and Maxillofacial Surgery of Bogomolets National Medical University). In September 2009 in the Sofia Kyiivska National Reserve was opened the sarcophagus of Yaroslav Mudryi and carried out:
- forensic medical description of the contents of the box with bones (Professor B.V.Mykhailychenko, MD A.M.Beliakov);
- morphological description of bones with the definition of gender (Professor V.G.Cherkasov, Associate Professors I.V.Dzevulska, O.I.Kovalchuk);
- morphological description of tooth-jaw apparatus (D.V.Topchii);
- x-ray research of the bones with the definition of age, gender and the presence of painful changes (Professor T.V.Topchii. X-ray research was conducted by the Kyiv city Bureau of forensic medical examination);
- immunological research of bone material with the definition of blood group (candidate of biological sciences R.O.Starovoitova, SI Main forensic Bureau of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine).
Complex studies have set up many interesting facts that require further study.
The Sofia Kyivska National Reserve was awarded Diplomas of specialists, who took part in the research of the skeletal remains in the sarcophagus of Yaroslav Mudryi at St. Sophia Cathedral.


Diplomas of the Sofia Kyivska National Reserve;
and MS, assistant A.M. Biliakov.



